Screenshots
Cross compiling 4tH:
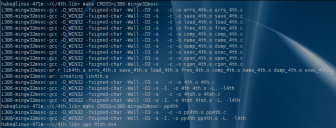
and running it:
MXE (M cross environment) is a GNU Makefile that compiles a cross compiler and cross compiles many free libraries such as SDL and Qt. Thus, it provides a nice cross compiling environment for various target platforms, which
Compiler and runtime: MinGW-w64.
| Target OS | Packages | |
|---|---|---|
| Static | Shared | |
| 32 bit Windows | 99% (379/381) | 72% (273/381) |
| 64 bit Windows | 94% (360/381) | 71% (271/381) |
These numbers were last updated on December 16, 2015. See the current status for individual packages.
Executables built for 32 bit Windows can be executed on 64 bit Windows as well.
How to choose MXE target:
Remark: The 'w64-mingw32' in those names are left-overs from historical evolutions in the open source cross-compilation world and refer in no way to the result being 64 or 32 bit Windows.
OpenMP (libgomp) and pthreads (winpthreads) are always available.
When building shared libraries, there are several approaches to recursively finding DLL dependencies (alphabetical list):
Experimental support for GCC with posix threads was added in November 2015. Since January 2019 it is used by default.
Experimental support for alternate GCC Exception Handling was added in February 2017.
First, you should ensure that your system meets MXE's requirements. You will almost certainly have to install some stuff.
When everything is fine, download the current version:
git clone https://github.com/mxe/mxe.git
If you don't mind installing it in your home directory, just skip the following step and go straight to step 3.
MXE builds and installs everything under the same top-level directory and is not relocatable after the first packages are built.
Due to limitations of GNU Make, the path of MXE is not allowed to contain any whitespace characters.
Now you should save any previous installation of the MXE. Assuming you've installed it under /opt/mxe (any other directory will do as well), you should execute the following commands:
su mv /opt/mxe /opt/mxe.old exit
Then you need to transfer the entire directory to its definitive location. We will assume again you use /opt/mxe, but feel free to use any other directory if you like.
su mv mxe /opt/mxe exit
We're almost done. Just change to your newly created directory and get going:
cd /opt/mxe
Enter the directory where you've downloaded MXE. Now it depends on what you actually want – or need.
If you choose to enter:
make
you're in for a long wait, because it compiles a lot of packages. On the other hand it doesn't require any intervention, so you're free to do whatever you like – like watch a movie or go for a night on the town. When it's done you'll find that you've installed a very capable Win32 cross compiler onto your system.
If you only need the most basic tools you can also use:
make cc
and add any additional packages you need later on. You can also supply a host of packages on the command line, e.g.:
make gtk lua libidn
Targets can also be specified on the command line. By default, only i686-w64-mingw32.static is built, but you can build your toolchain(s) of choice with:
make MXE_TARGETS='x86_64-w64-mingw32.static i686-w64-mingw32.static'
or by adjusting the MXE_TARGETS variable
in settings.mk.
You'll always end up with a consistent cross compiling environment.
If you have trouble here, please feel free to contact the mxe team through the issue tracker or mailing list.
After you're done it just needs a little post-installation.
Instead of building MXE packages from source, you can install packages from our APT repository for the following distros:
See the distro list for current codenames and last build dates.
Ensure required tools are available (usually installed by default):
sudo apt-get install \
software-properties-common \
lsb-release
Add and refresh MXE repository:
sudo apt-key adv \
--keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com \
--recv-keys 86B72ED9 && \
sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://pkg.mxe.cc/repos/apt `lsb_release -sc` main" && \
sudo apt-get update
Note that all package and target names have underscores replaced with dashes. For example:
apt-cache search 'mxe.*sdl_net'
outputs:
mxe-i686-w64-mingw32.shared-sdl-net - MXE package sdl_net for i686-w64-mingw32.shared mxe-i686-w64-mingw32.static-sdl-net - MXE package sdl_net for i686-w64-mingw32.static mxe-x86-64-w64-mingw32.shared-sdl-net - MXE package sdl_net for x86_64-w64-mingw32.shared mxe-x86-64-w64-mingw32.static-sdl-net - MXE package sdl_net for x86_64-w64-mingw32.static
Install the basic cross-compiler:
sudo apt-get install \
mxe-{i686,x86-64}-w64-mingw32.{static,shared}-cc
Confirm installation (note standard MXE target naming for tools):
PATH=/usr/lib/mxe/usr/bin:$PATH \
x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-gcc --version
outputs:
x86_64-w64-mingw32.static-gcc (GCC) 5.5.0 Copyright (C) 2015 Free Software Foundation, Inc. This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
See the Lightspark project for examples of:
Edit the appropriate config script (.bashrc, .cshrc, .profile, .zshrc, etc.) for your shell in order to change $PATH:
export PATH=/where MXE is installed/usr/bin:$PATH
You may be tempted to also add $(TARGET)/bin
to your path. You never want to do this,
the executables and scripts in there will cause conflicts
with your native toolchain.
In case you are using custom $PKG_CONFIG_PATH entries, you can add separate entries for cross builds:
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH="entries for native builds"
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH_i686_w64_mingw32_static="entries for MXE builds"
Remember to use i686-w64-mingw32.static-pkg-config instead of pkg-config for cross builds. The Autotools do that automatically for you.
Note that any other compiler related environment variables (like $CC, $LDFLAGS, etc.) may spoil your compiling pleasure, so be sure to delete or disable those.
For the most isolated and repeatable environment, use a white-list approach:
unset `env | \
grep -vi '^EDITOR=\|^HOME=\|^LANG=\|MXE\|^PATH=' | \
grep -vi 'PKG_CONFIG\|PROXY\|^PS1=\|^TERM=' | \
cut -d '=' -f1 | tr '\n' ' '`
Congratulations! You're ready to cross compile anything you like.
If you use the Autotools, all you have to do is:
./configure --host=i686-w64-mingw32.static make
If you build a library, you might also want to enforce a static build:
./configure --host=i686-w64-mingw32.static --enable-static --disable-shared make
Don't worry about a warning like this:
configure: WARNING: If you wanted to set the --build type, don't use --host. If a cross compiler is detected then cross compile mode will be used.
Everything will be just fine.
If you have a CMake project, you can use the provided cmake wrapper:
i686-w64-mingw32.static-cmake ...
This will automatically use the MXE version of cmake and locate the toolchain file.
If you have a Qt application, all you have to do is:
/<where-MXE-is-installed>/usr/i686-w64-mingw32.static/qt5/bin/qmake make
Note that Qt 5 is in the "qt5" subdirectory. Qt 4 is in the "qt" subdirectory and its qmake can be invoked similarly.
If you are using Qt plugins such as the svg or ico image handlers, you should also have a look at the Qt documentation about static plugins.
Qt 4 only: Sql drivers (-qt-sql-*) and image handlers for jpeg, tiff, gif and mng are built-in, not plugins.
If you have a handwritten Makefile, you probably will have to make a few adjustments to it:
CC=$(CROSS)gcc LD=$(CROSS)ld AR=$(CROSS)ar PKG_CONFIG=$(CROSS)pkg-config
You may have to add a few others, depending on your project.
Then, all you have to do is:
make CROSS=i686-w64-mingw32.static-
That's it!
Using static OpenSceneGraph libraries requires a few changes to your source. The graphics subsystem and all plugins required by your application must be referenced explicitly. Use a code block like the following:
#ifdef OSG_LIBRARY_STATIC USE_GRAPHICSWINDOW() USE_OSGPLUGIN(<plugin1>) USE_OSGPLUGIN(<plugin2>) ... #endif
Look at examples/osgstaticviewer/osgstaticviewer.cpp in the
OpenSceneGraph source distribution for an example. This example can be
compiled with the following command:
i686-w64-mingw32.static-g++ \
-o osgstaticviewer.exe examples/osgstaticviewer/osgstaticviewer.cpp \
`i686-w64-mingw32.static-pkg-config --cflags openscenegraph-osgViewer openscenegraph-osgPlugins` \
`i686-w64-mingw32.static-pkg-config --libs openscenegraph-osgViewer openscenegraph-osgPlugins`
The i686-w64-mingw32.static-pkg-config command from MXE will
automatically add -DOSG_LIBRARY_STATIC to your compiler flags.
If you need further assistance, feel free to join the mailing list where you'll get in touch with the MXE developers and other users.
To obtain the current version, run:
git clone https://github.com/mxe/mxe.git
To retrieve updates, run:
git pull
You can also browse the web repository.
In addition, feel free to join the mailing list and to propose new packages.
MXE requires a recent Unix system where all components as stated in the table below are installed. It also needs roughly 2 GiB of RAM to link gcc and at least 700 MB of disk space per target (counted with only gcc built).
Detailed instructions are available for:
| Autoconf | ≥ 2.68 |
| Automake | ≥ 1.11.3 |
| Bash | |
| Bison | |
| Bzip2 | |
| Flex | ≥ 2.5.31 |
| GCC (gcc, g++) | |
| gdk-pixbuf | |
| Git | ≥ 1.7 |
| GNU Coreutils | |
| GNU Gettext | |
| GNU gperf | |
| GNU Make | ≥ 3.81 |
| GNU Sed | |
| GNU Tar | |
| Intltool | ≥ 0.40 |
| LibC for 32-bit | |
| Libtool | ≥ 2.2 |
| Lzip | |
| Mako Templates | |
| OpenSSL-dev | ≥ 1.01 |
| p7zip (7-Zip) | |
| Patch | |
| Perl | |
| Perl XML::Parser | |
| Python3 | |
| Ruby | |
| UnZip | |
| Wget | |
| XZ Utils | |
| zlib | ≥ 1.20 |
apk add \
autoconf \
automake \
bash \
binutils \
bison \
bzip2 \
flex \
g++ \
gdk-pixbuf \
gettext \
git \
gperf \
intltool \
libtool \
linux-headers \
lzip \
make \
openssl \
openssl-dev \
p7zip \
patch \
perl \
python3 \
py3-mako \
ruby \
unzip \
wget \
xz \
zlib
apt-get install \
autoconf \
automake \
autopoint \
bash \
bison \
bzip2 \
flex \
g++ \
g++-multilib \
gettext \
git \
gperf \
intltool \
libc6-dev-i386 \
libclang-dev \
libgdk-pixbuf2.0-dev \
libltdl-dev \
libgl-dev \
libpcre2-dev \
libssl-dev \
libtool-bin \
libxml-parser-perl \
lzip \
make \
openssl \
p7zip-full \
patch \
perl \
python3 \
python3-mako \
python3-packaging \
python3-pkg-resources \
python3-setuptools \
python-is-python3 \
ruby \
sed \
sqlite3 \
unzip \
wget \
xz-utils
On 32-bit installs and on arm64 installs,
g++-multilib
libc6-dev-i386
are not required, however there are potential issues with 32-bit systems.
Only the latest Debian stable series is supported.
You can install binary MXE packages from our APT repository.
Ensure Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) is installed/available. On some systems, it may be as simple as:
yum install epel-release
yum install \
autoconf \
automake \
bash \
bison \
bzip2 \
flex \
gcc-c++ \
gdk-pixbuf2-devel \
gettext \
git \
gperf \
intltool \
libtool \
lzip \
make \
mesa-libGL-devel \
openssl \
openssl-devel \
p7zip \
patch \
perl \
python3 \
python3-mako \
ruby \
sed \
unzip \
wget \
which \
xz
On 64-bit Fedora, there are issues without a 32-bit compiler.
pkg install \
autoconf \
automake \
bash \
bison \
coreutils \
flex \
gcc \
gdk-pixbuf2 \
gettext \
git \
glib \
gmake \
gperf \
gsed \
intltool \
libtool \
openssl \
p5-XML-Parser \
p7zip \
patch \
perl5 \
python3 \
textproc/py-mako \
ruby \
unzip \
wget
Use gmake instead of make.
Install file(1) from ports, because file(1) from base works very-very-very slow with long text files.
Do not build as root. See #902.
Ensure that /usr/local/bin precedes /usr/bin in your $PATH:
For C style shells, edit .cshrc
setenv PATH /usr/local/bin:$PATH
For Bourne shells, edit .profile
export PATH=/usr/local/bin:$PATH
On 64-bit FreeBSD, there are issues without a 32-bit compiler.
N.B. FreeBSD is no longer fully supported
to build the remainder of MXE, run:
gmake EXCLUDE_PKGS='gtksourceviewmm2 ocaml% openexr pcl qtbase'
to see a list of all dependent downstream packages that will be excluded, run:
gmake show-downstream-deps-'gtksourceviewmm2 ocaml% openexr \
pcl qtbase'
pacman-g2 -S \
autoconf \
automake \
bash \
bison \
bzip2 \
flex \
gcc \
gdk-pixbuf2\
gettext \
git \
gperf \
intltool \
libtool \
lzip \
make \
openssl \
patch \
perl \
perl-xml-parser \
python3 \
python3-mako \
ruby \
sed \
unzip \
wget \
xz \
xz-lzma
On 64-bit Frugalware, there are issues without a 32-bit compiler.
emerge \
app-arch/bzip2 \
app-arch/lzip \
app-arch/p7zip \
app-arch/unzip \
app-arch/xz-utils \
app-shells/bash \
dev-lang/perl \
dev-lang/python \
dev-lang/ruby \
dev-libs/openssl \
dev-perl/XML-Parser \
dev-python/mako \
dev-util/gperf \
dev-util/intltool \
dev-vcs/git \
net-misc/wget \
sys-apps/sed \
sys-devel/autoconf \
sys-devel/automake \
sys-devel/bison \
sys-devel/flex \
sys-devel/gcc \
sys-devel/gettext \
sys-devel/libtool \
sys-devel/make \
sys-devel/patch \
x11-libs/gdk-pixbuf
Install the latest Xcode
Install MacPorts, then run:
sudo port -N install \
coreutils \
gdk-pixbuf2 \
gnutar \
gsed \
intltool \
lzip \
p7zip \
pkgconfig \
py-mako \
wget \
xz
Rudix has shut down since August 2018
Install Homebrew, then run:
brew install \
autoconf \
automake \
coreutils \
gdk-pixbuf \
gnu-sed \
gnu-tar \
intltool \
libtool \
lzip \
pkg-config \
python3 \
p7zip \
wget \
xz
python3 -m pip install mako
You will see messages about
keg-only
formulae and tools prefixed with 'g' - you can safely ignore these
and no homebrew related $PATH modifications or
brew links are necessary.
You may be prompted to install a java runtime - this is not required.
Mac OS X versions ≤ 10.9 are no longer tested.
For Xcode <7.3, run:
make EXCLUDE_PKGS='nsis'
zypper install -R \
autoconf \
automake \
bash \
bison \
bzip2 \
flex \
gcc-32bit \
gcc-c++ \
gdk-pixbuf-devel \
gettext-tools \
git \
glibc-devel-32bit \
gperf \
intltool \
libgcc46-32bit \
libgomp46-32bit \
libopenssl-devel \
libstdc++46-devel-32bit \
libtool \
lzip \
make \
openssl \
p7zip \
patch \
perl \
perl-XML-Parser \
python3 \
python3-Mako \
ruby \
sed \
unzip \
wget \
xz
On 32-bit installs,
gcc-32bit
glibc-devel-32bit
libgcc46-32bit
libgomp46-32bit
libstdc++46-devel-32bit
are not required, however there are potential issues with 32-bit systems.
xbps-install -S \
autoconf \
automake \
flex \
gcc \
gdk-pixbuf-devel \
gettext \
gettext-devel \
git \
gperf \
intltool \
libcurl-devel \
libtool \
lzip \
make \
p7zip \
patch \
perl-XML-Parser \
pkgconf \
python3 \
python3-Mako \
ruby \
unzip \
wget \
xz
Install the Windows Subsystem for Linux, noting that WSL1 does not support 32-bit code execution.
If mixing WSL1 and WSL2, ensure the distro-specific or global defaults are set.
Requirements should match the Debian, Fedora, openSUSE etc. sections
above, but care should be taken to ensure MXE is installed in the
Linux subsystem under / instead of the mounted Windows
folders in /mnt.
It can be made to work using symlinks and specifying:
make MXE_TMP=/tmp/mxe-tmp ...
See further reading in:
Certain packages contain native tools that are currently 32-bit only. In order to build these on a 64-bit system, multi-lib support must be enabled in the compiler toolchain. However, not all operating systems support this.
To build the remainder of MXE, specify the affected packages to exclude:
make EXCLUDE_PKGS='ocaml%'
All build commands also download the packages if necessary.
In a BSD userland, substitute "make" with "gmake" as all commands are based on GNU Make.
settings.mk
LOCAL_PKG_LIST := foo bar .DEFAULT_GOAL := local-pkg-list local-pkg-list: $(LOCAL_PKG_LIST)
make will only build those packages (and their
dependencies, of course)
settings.mk and defaults to the number
of CPUs up to a max of 6 to prevent runaway system
load with diminishing returns - see the
GNU Make manual
for more details on parallel execution
The package should be a free software library that is really used by one of your applications. Please also review our legal notes.
BTW, we're always curious about the applications people are porting. We maintain a list of projects which use MXE. No matter whether your project is free or proprietary – as long as it has its own website, we'd be happy to link to it.
Also, feel free to link to us. :-)
Grep through the src/*.mk files
to find a project that is most similar to yours.
(Really, grep is your friend here.)
For instance, when adding a GNU library, you should take a package like gettext.mk or libiconv.mk as the base of your work. When using a SourceForge project, you could start with a copy of xmlwrapp.mk. And so on.
GitHub hosted projects can automatically configure updates,
urls, file names etc. by setting $(PKG)_GH_CONF
instead of $(PKG)_FILE, $(PKG)_SUBDIR, $(PKG)_URL, and
$(PKG)_UPDATE sections.
To track releases set:
$(PKG)_GH_CONF := owner/repo/releases[/latest][, tag prefix, tag suffix, tag filter-out, version separator]
Releases may require setting _FILE, _SUBDIR, _URL, depending on the naming convention used by the project for tarballs.
To track tags set:
$(PKG)_GH_CONF := owner/repo/tags[, tag prefix, tag suffix, tag filter-out, version separator]
To track branches, set:
$(PKG)_GH_CONF := owner/repo/branches/<branch name>
See the following packages for examples:
The GNU Make Standard Library is also available (though it should be unnecessary for most packages).
Alternatively you can use tool tools/skeleton.py to
create a skeleton of new MXE package. It fills most of the fields
of .mk file automatically and supports typical
build scenarios through option --builder. It also
adds a package to the list of packages
(see below).
Adjust the comments,
fill in the $(PKG)_* fields.
To fill the $(PKG)_CHECKSUM field, use a command such as (for file gettext.mk):
make update-checksum-gettext
or:
openssl sha256 pkg/gettext-x.y.z.tar.gz
if you have already downloaded the package.
Be especially careful with the $(PKG)_DEPS section.
The easiest way to get the dependencies right
is to start with a minimal setup.
That is,
initialize MXE with make cc only,
then check whether your package builds successfully.
Always list the dependency on cc explicitly:
$(PKG)_DEPS := cc ...
Specify official name and website of a package.
If the official name coincides with the package name,
you can omit $(PKG)_DESCR.
PKG := libdvdetect $(PKG)_WEBSITE := https://www.dvdetect.de/ $(PKG)_DESCR := Fast database lookup for DVDs
Always look for the SSL version of URLs, that is,
prefer https:// URLs over http:// URLs.
Write your $(PKG)_BUILD.
If your library has a ./configure script,
enable/disable all dependency libraries explicitly
via "--enable-*" and "--disable-*" options.
Things not to do:
Useful Makefile variables provided by MXE:
$(SOURCE_DIR)
is a directory with package source and
$(BUILD_DIR)
is an empty directory intended for build files.
Both directories are temporary.
Prefer out-of-tree builds. Autotools
and CMake support them.
$(PREFIX)
is path to usr/ directory.
$(TOP_DIR)
is path to MXE root directory.
$(TARGET) is target triplet
(e.g., i686-w64-mingw32.static).
$(BUILD) is build triplet
(e.g., x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu).
$(MXE_CONFIGURE_OPTS)
adds standard options to ./configure script.
Typical usage:
cd '$(BUILD_DIR)' && '$(SOURCE_DIR)'/configure \
$(MXE_CONFIGURE_OPTS)
$(MXE_DISABLE_CRUFT)
disables installation of documentation and programs.
$(MAKE) -C '$(BUILD_DIR)' -j '$(JOBS)' $(MXE_DISABLE_CRUFT)
$(MAKE) -C '$(BUILD_DIR)' -j 1 install $(MXE_DISABLE_CRUFT)
$(BUILD_SHARED)
is TRUE for shared targets. Useful to add flags applicable
only to shared targets.
$(if $(BUILD_SHARED),LDFLAGS=-no-undefined)
Similarly,
$(BUILD_STATIC)
is TRUE for static targets;
$(BUILD_NATIVE)
is TRUE for native targets;
$(BUILD_CROSS)
is TRUE for cross targets.
You might also have to provide a patch for it. In that case, have a look at other patches such as sdl2-2-libtool.patch. In particular, each patch file should be named as:
PACKAGE-PATCHNUMBER-DESCRIPTION.patch
and should start with:
This file is part of MXE. See LICENSE.md for licensing information. This patch has been taken from: https://...
where the URL points to the bugtracker entry, mailing list entry or website you took the patch from.
If you created the patch yourself, please offer it to the upstream project first, and point to that URL, using the same wording: "This patch has been taken from:".
Depending on the feedback you get from the upstream project, you might want to improve your patch.
If you find some time, please provide a minimal test program for it. It should be simple, stand alone and should work unmodified for many (all?) future versions of the library. Test programs are named as:
PACKAGE-test.cor
PACKAGE-test.cpp
depending on whether it is a C or C++ library. To get a clue, please have a look at existing test programs such as sdl-test.c.
At the very end of your *.mk file
you should build the test program in a generic way,
using strict compiler flags.
The last few lines of
sdl.mk
will give you a clue.
You could also try to provide a $(PKG)_UPDATE section.
However, that requires some experience and "feeling" for it.
So it is perfectly okay if you leave a placeholder:
define $(PKG)_UPDATE
echo 'TODO: write update script for $(PKG).' >&2;
echo $($(PKG)_VERSION)
endef
We'll fill that in for you. It's a funny exercise.
Check that you don't have "dirty stuff" in your *.mk files,
such as TAB characters or trailing spaces at lines endings. Run:
make cleanup-style
to remove these.
Have a look at random *.mk files
to get a feeling for the coding style.
The same holds for your test program.
However, patch files should always appear in the same coding style as the files they are patching.
When patching sources with crlf line endings, the patch
file itself should also have the same eol style. Use the
convention of naming the file as *crlf.patch
to instruct git not to normalise the line endings (defined
in .gitattributes).
Finally, in your $(PKG)_BUILD section,
please check that you use our portability variables:
bash | → | $(SHELL) |
date | → | $(DATE) |
install | → | $(INSTALL) |
libtool | → | $(LIBTOOL) |
libtoolize | → | $(LIBTOOLIZE) |
make | → | $(MAKE) |
patch | → | $(PATCH) |
sed | → | $(SED) |
sort | → | $(SORT) |
wget | → | $(WGET) |
Check whether everything runs fine.
If you have some trouble,
don't hesitate to ask on the
mailing list,
providing your *.mk file so far.
Issue a
pull request
to propose your final *.mk file to us.
If you have trouble with pull requests,
send your file to the mailing list instead.
Either way,
don't forget to tell us
if there are some pieces in your *.mk file
you feel unsure about.
We'll then have a specific look at those parts,
which avoids trouble for you and us in the future.
(contact via the project mailing list)
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Modern legal systems are like any other large, complex, and evolving body of code you're likely to encounter.
They have their own language with quirky parsers, compilers, and interpreters (though these tend to be human). Their issue trackers are a backlog of court cases. They have bugs. They have traps for the uninitiated that may potentially do more than waste your time.
We currently limit ourselves to:
--enable-languages='c,c++,objc,fortran'
so nothing mentioned here or on the mailing list should be taken as legal advice. :-)
The best starting point for any legal questions would be the
FTF (Freedom Task Force of the FSFE (Free Software Foundation Europe)).
They have been very helpful in the past, and maintain an extensive network of legal contacts, both within and outside Europe.
Your local jurisdiction may be a signatory to various international agreements, so be sure to mention where you are in any correspondence (much like any detailed bug report really).
Additionally, you should also do some background reading from the FSF (Free Software Foundation) and Wikipedia to familiarise yourself with some of the potential issues (and experience some context-switching overhead).
Contributions are always welcome!
Ownership of all contributions (bug fixes, new packages, doc updates, etc.) remain with the author. All we require is a real name (no l33t handles, please), and that you release your work under our licence.
If you prefer not to be credited with a contribution, please notify the committer.
Each package is individually licensed under terms specified by the authors of that package. Please see the respective source tarball and/or project website for details.
Packages that are non-free or ambiguous will be removed or rejected.
The definition of free must be one of:
Please contact the mailing list if you notice a package that doesn't meet these guidlines.
In addition to the usual considerations (copyrights, patents, trademarks, export regulations etc.), building statically linked libraries for Windows exposes some edge cases that you may not have encountered before.
According to freedom 0 and our own licence, you can use mxe in countless different environments, each with it's own special legal considerations. The configuration options of certain packages (e.g ffmpeg) allow the use of non-free software and/or combinations that cause license violations.
For these packages, we will provide sensible defaults aimed at achieving the following goals:
Note that this does not prevent downstream violations, or affect any further obligations a licence may impose on you.
Review the FAQ
Review the Differences from the GPL section of the Wikipedia article mentioned above.
See conflicting accounts from the FSF and the OpenSSL project.
Since August 2015, there is an ongoing effort to re-license to Apache v2.
The FDK license has a "no charging fees" clause that likely violates the GPL.
The stable branch was retired as it did more harm than good. Everybody is using the master branch, because it is always recent and well enough tested. For historical reference, the last commit to the stable branch was 0c6cc9c, which was fully merged into master as usual.
Added support for shared toolchains for over 50% of all the packages.
Unfortunately, a number of factors have forced us to drop support for MinGW 3 (i.e. "MinGW.org"), in favor of the MinGW-w64 toolchain. This decision was made in a large part because of the dropping of support for MinGW by GLib and Qt5, which arguably are two of the most important packages in MXE. Other considerations have also been taken, like the lack of maintainership in MinGW and potential legal challenges that comes with using supplemental DirectX headers in MinGW in order to support Qt4. Worse yet, having to support the unsupported MinGW toolchain impedes adding or updating packages, as shown in the pull request of updating GLib.
Please note that dropping support for MinGW DOES NOT MEAN dropping support for the 32-bit architecture. MinGW-w64 also supports 32-bit target through i686-w64-mingw32.
To ease migration to the supported MinGW-w64 target, we have
finished porting all packages that were MinGW-only to at least
i686-w64-mingw32 (32-bit target of MinGW-w64). Hence your existing
commands should work out-of-the-box assuming the
MXE_TARGETS environment variable is set correctly.
The stable branch was updated to the current development version after a thorough testing phase.
Current users are strongly encouraged to start with a clean tree as the toolchain has been updated and requires a full rebuild:
git pull && make clean && make
Most packages were updated to their latest version.
Many new packages are supported: alure, apr-util, apr, armadillo, cegui, cfitsio, cminpack, flann, gtkglarea, gtkimageview, harfbuzz, hdf4, hdf5, hunspell, icu4c, itk, lensfun, levmar, libf2c, libftdi, libgda, libgdamm, libglade, liblqr-1, libmodplug, librtmp, libzip, log4cxx, mdbtools, ncurses, netcdf, netpbm, ocaml-cairo, ocaml-camlimages, ocaml-core, ocaml-findlib, ocaml-flexdll, ocaml-lablgl, ocaml-lablgtk2, ocaml-native, ocaml-xml-light, opencv, opus, opusfile, pcl, picomodel, plib, plibc, poppler, portablexdr, portmidi, protobuf, qdbm, qt5, qtactiveqt, qtbase, qtdeclarative, qtgraphicaleffects, qtimageformats, qtjsbackend, qtmultimedia, qtquick1, qtquickcontrols, qtscript, qtsensors, qtserialport, qtsvg, qttools, qttranslations, qtxmlpatterns, qwt, sdl_gfx, sfml, sox, teem, twolame, vtk6, wavpack, wget, winpthreads, xapian-core, yasm
Added support for mingw-w64 based toolchains targeting 32 & 64-bit architectures.
With the addition of Qt5, there is no longer a prefixed version of qmake, see the Qt section of the tutorial for the new way to invoke qmake.
FreeBSD is no longer fully supported. Qt5, ocaml*, and 8 other packages are excluded from the build.
The release tarballs have been replaced with a stable branch that conforms to the new branch concept:
The project has been renamed from mingw-cross-env (MinGW cross compiling environment) to MXE (M cross environment).
Most packages were updated to their latest version.
New packages are supported: agg, cgal, eigen, file, gta, json-c, libgnurx, libharu, libircclient, libssh2, libxml++, llvm, lzo, mpfr, nettle, opencsg, qjson, qwtplot3d, vtk, and wt.
Minor bugfixes in several packages.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
Packages gtkmm and gtksourceviewmm have been renamed to gtkmm2 and gtksourceviewmm2.
New packages are supported: libass, poco, and t4k_common.
This release fixes a download error caused by the pixman project (a sudden change of their URL scheme without proper redirects). That sort of thing should never happen!
The download mechanisms are improved.
A CMake toolchain file is provided to simplify cross-compiling projects which use CMake.
Support for Debian/Lenny is dropped.
Package gtk is renamed to gtk2.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
New packages are supported: dbus, graphicsmagick, libical, liboauth, physfs, and vigra.
Note for boost::filesystem users:
Version 3 is a major revision
and now the default in 1.46.
This release fixes a checksum error caused by the atkmm project (a sudden change of their current source tarball). That sort of thing should never happen!
This release provides some improvements of the build system such as an automatic check for most of the requirements.
All packages are updated to their latest version.
New packages are supported: bfd, blas, cblas, dcmtk, ftgl, lapack, lcms1, mingw-utils, mxml, suitesparse and tinyxml.
This release provides lots of improvements to the build system as well as the documentation.
Support for OpenSolaris is dropped.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
Many new packages are supported: atkmm, cairomm, cunit, faac, faad2, ffmpeg, gdk-pixbuf, glibmm, gtkglextmm, gtkmm, gtksourceview, gtksourceviewmm, imagemagick, lame, libiberty, libsigc++, libvpx, matio, openal, opencore-amr, pangomm, pfstools, plotmm, sdl_sound and x264.
This release fixes download errors caused by the Qt project (a sudden change of their current source tarball).
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
This release fixes download errors caused by the MinGW project (a sudden change of their URL scheme without proper redirects). That sort of thing should never happen!
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
New packages are supported: libarchive, libgee and xvidcore.
This release switches back from TDM to the official GCC, thus supporting the current GCC 4.5.
The set of DirectX headers is improved and more complete.
The deadlock issues with Pthreads-w32 are fixed.
A static build of GDB is provided, i.e. a standalone "gdb.exe" that doesn't require any extra DLLs.
More packages are backed by test programs.
Many "sed hacks" are replaced by proper portability patches.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
Many new packages are supported: fribidi, gc, gdb, gmp, gsl, gst-plugins-base, gst-plugins-good, gstreamer, gtkglext, guile, libcroco, libffi, liboil, libpaper, libshout, libunistring and xine-lib.
This release fixes some minor build issues, and contains a first small set of test programs to check the package builds.
The build rules are simplified by calling generators like Autotools and Flex, instead of patching the generated files.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
Many new packages are supported: aubio, devil, directx, exiv2, fftw, freeimage, gsoap, id3lib, liblo, libpano13, librsvg, libsamplerate, muparser, openscenegraph, portaudio and sdl_pango.
This release contains a packaging bug. Please use release 2.12 instead.
This release adds support for many new packages: flac, libmad, libsndfile, sdl_net, speex, postgresql, freetds, openssl, plotutils, taglib, lcms, freeglut, xerces and zziplib.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
In addition to the libraries some command line tools such as psql.exe are built, too.
The placements of logfiles, as well as many other build details, have been improved.
This release adds support for Qt, VMime and libmng.
The target triplet is updated to i686-pc-mingw32.
OpenMP support is enabled in GCC.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
This release comes with a better look & feel by providing a highlevel overview of the build process.
The detailed build messages are stored into separate log files for each package, so parallel builds don't intermix them anymore.
The download URLs of SourceForge packages are adjusted to ensure that the selected SourceForge mirror is really used and not circumvalented via HTTP redirects to other mirrors.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
The whole mingw-cross-env project has moved to Savannah. So all URIs have changed, but the old URIs redirect to the new locations seamlessly.
Everyone is invited to join the freshly created project mailing list.
This release provides an improved version recognition for SourceForge packages. SourceForge changed their page layout in a way that makes it much harder to identify the current version of a package.
Additionally, almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
This release contains some portability fixes which allow it to run on a wider range of systems such as Frugalware.
The documentation and website are completely revised.
New packages such as CppUnit, libUsb, NSIS, Popt, SQLite and Theora are supported.
Almost all packages are updated to their latest version.
A new command "make download" is implemented.
This release fixes a download error caused by the MinGW project. They suddenly changed the names of their source tarballs. That sort of thing should never happen!
This release also contains some bugfixes which allow it to run on a wider range of systems.
All downloaded files are now verified by their SHA-1 checksums.
New versions of various packages are supported.
This release provides many new libraries such as wxWidgets, GTK+ and OpenEXR.
In addition, new versions of various packages are supported.
This release fixes some serious build problems on FreeBSD and MacOS-X.
The Makefile has a new target "clean-pkg" and allows to be called from a separate build directory via "make -f .../Makefile".
Some new versions of the packages are supported, especially GCC-4.3 by switching from MinGW GCC to TDM-GCC.
This release fixes some minor build problems.
It also supports some new packages and some newer versions of the already supported packages.
Parallelization is now disabled by default.
This release fixes a download error caused by the GDAL project. They suddenly changed their download URLs. That sort of thing should never happen!
In addition, some newer versions of various packages are supported.
There is also a small compatibility fix for OS X.
The shell script has been rewritten as Makefile and supports partial builds and parallel builds.
As usual, this release also supports some new packages and some newer versions of the already supported packages.
This release now includes a tutorial by Hans Bezemer and has improved compile options of FLTK. As usual, it supports some newer versions of the libraries.
At the request of its author, libowfat is no longer supported from this release on.
The script now uses a specific SourceForge mirror instead of randomly chosen ones, because the download phase often stumbled on some very slow mirrors.
A sudden change in the download URLs of GEOS made the automatic download fail. Such changes should never happen! But it happened, and this quick release is an attempt to limit the damage.
This release also supports some newer versions of the libraries including support for fontconfig-2.5.0.
This release is a switch from gcc-3 to gcc-4. It also supports a new library and some newer versions of the already supported libraries.
This release is the result of the public attention the release 1.0 got. It contains many improvements suggested by its first users, and adds support for many new libraries.
Thanks to Rocco Rutte who contributed many code snippets.
This first release has been created in a 7-day-sprint.